Cycle of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems - Food webs are models that demonstrate how matter and energy is transferred between producers, consumers, and decomposers as the three groups interact within an ecosystem. Transfers of matter into and out of the physical environment occur at every level. Decomposers recycle nutrients from dead plant or animal matter back to the soil in terrestrial environments or to the water in aquatic environments. The atoms that make up the organisms in an ecosystem are cycled repeatedly between the living and nonliving parts of the ecosystem.
Cycle of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems - Food webs are models that demonstrate how matter and energy is transferred between producers, consumers, and decomposers as the three groups interact within an ecosystem. Transfers of matter into and out of the physical environment occur at every level. Decomposers recycle nutrients from dead plant or animal matter back to the soil in terrestrial environments or to the water in aquatic environments. The atoms that make up the organisms in an ecosystem are cycled repeatedly between the living and nonliving parts of the ecosystem.: Overview
This topic covers various concepts like Food Chains, Food Webs, etc.
Important Questions on Cycle of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems - Food webs are models that demonstrate how matter and energy is transferred between producers, consumers, and decomposers as the three groups interact within an ecosystem. Transfers of matter into and out of the physical environment occur at every level. Decomposers recycle nutrients from dead plant or animal matter back to the soil in terrestrial environments or to the water in aquatic environments. The atoms that make up the organisms in an ecosystem are cycled repeatedly between the living and nonliving parts of the ecosystem.
An ecosystem, such as an aquarium, is self-sustaining if it involves the interaction between organisms, a flow of energy, and the presence of
What is a food web?
Use the words, given in the box, to make a ‘food chain’. Also, identify the nature (terrestrial/aquatic) of the food chain.
| shark | fish | seal | algae |
_____ → _____ → _____ → _____
Use the words, given in the box, to make a ‘food chain’. Also, identify the nature (terrestrial/aquatic) of the food chain.
| dolphin | snail | tuna | plankton |
_____ → _____ → _____ → _____
Use the words, given in the box, to make a ‘food chain’. Also, identify the nature (terrestrial/aquatic) of the food chain.
| owl | grass | grasshopper | rat | snake |
_____ _____ _____ _____ _____
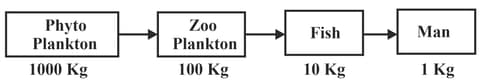
This flow chart represents: _____.
Why is balance or equilibrium necessary in a food web?
What will be the amount of energy available to the organisms of the second trophic level of a food chain, if the energy available at the first trophic level is 10,000 joules?
How much energy will be available to hawks in the food chain comprising mice,snake, paddy and hawks, if 20,000.J of energy is available to paddy from the sun?
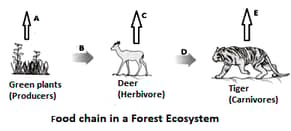
In the following food chain, vertical arrows indicate the energy lost to the environment and horizontal arrows indicate energy transferred to the next trophic level. Which one of the three vertical arrows (A, C and E) and which one of the two horizontal arrows (B and D) will represent more energy transfer? Give reason for your answer.
Depict the food chain of Antarctic ocean.
A genet is a herbivorous animal.
Explain the food habit of genet.
Explain the flow of energy through African Savanna.
Depict the food web of African Savanna.
Choose the tertiary consumer of Madagascar food chain.
Explain about the producers in the Antarctic ocean.
Assertion: A network of food chains existing together in an ecosystem is known as food web.
Reason: An animal like Kite cannot be part of food web.
Name the three main types of food chain in an ecosystem.
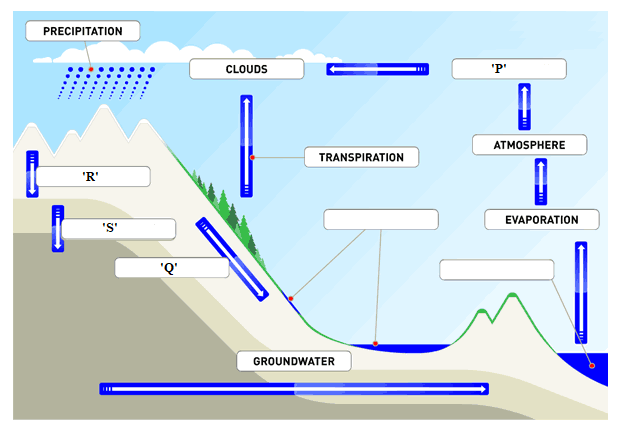
Study the picture above and identify which letter indicates infiltration:
